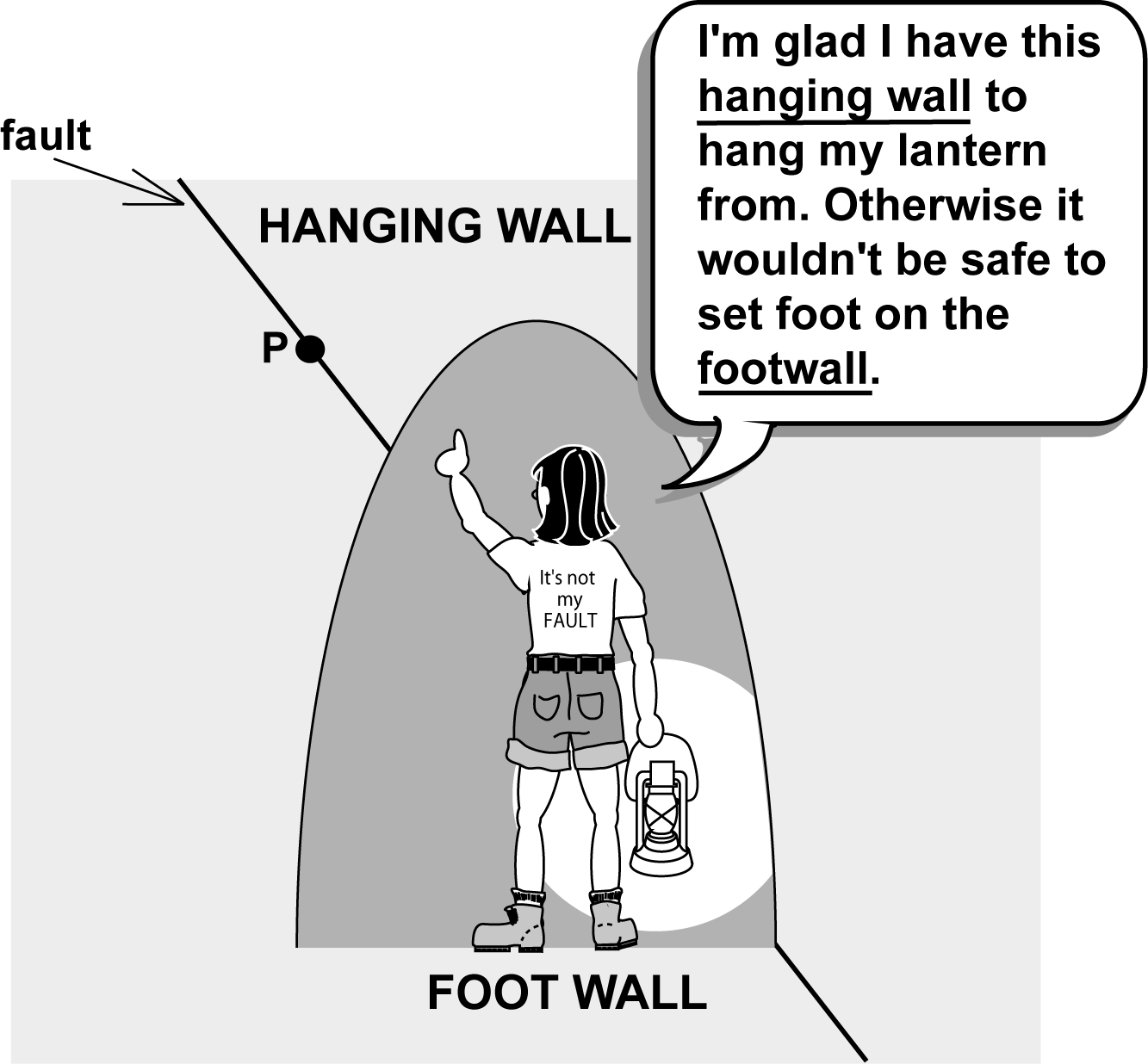
What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall . normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. in normal faults, the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall (figure 13 and figure 14). The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. the body of rock above the fault is called the hanging wall, and the body of rock below it is called the footwall. If the hanging wall moves sideways, parallel. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall. Thrust faults are reverse faults that dip less than 45°. reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. a reverse/thrust fault is a geological fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall due to compressional forces, often associated with convergent plate boundaries. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. If the fault develops in a situation of. These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. The steep face of an exposed block is called the fault scarp. This type of fault can result in significant geological features and can also generate powerful seismic events. Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments;
from geol319r4.athabascau.ca
the body of rock above the fault is called the hanging wall, and the body of rock below it is called the footwall. in normal faults, the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall (figure 13 and figure 14). These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. The steep face of an exposed block is called the fault scarp. They are common at convergent boundaries. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. This type of fault can result in significant geological features and can also generate powerful seismic events. reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together.
Unit 4 GEOL 319
What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. The steep face of an exposed block is called the fault scarp. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. a reverse/thrust fault is a geological fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall due to compressional forces, often associated with convergent plate boundaries. This motion can be determined by tracing the. Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments; The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. They are common at convergent boundaries. We identify the hanging and foot walls relative to the fault plane. If the fault develops in a situation of. If the hanging wall moves sideways, parallel. reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. the body of rock above the fault is called the hanging wall, and the body of rock below it is called the footwall. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall.
From www.researchgate.net
3D model showing fault surface, hangingwall and footwall before What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall If the fault develops in a situation of. They are common at convergent boundaries. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. Thrust faults with. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Structural Geology Stress and Strain PowerPoint Presentation What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall The steep face of an exposed block is called the fault scarp. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall. the body of rock above the fault is called the hanging wall, and the body of rock below it is called the footwall. This type of fault can result in significant geological. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.thoughtco.com
Learn About Different Fault Types What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall This motion can be determined by tracing the. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. Thrust faults are reverse faults that dip less than 45°. The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. the body of rock above the fault is called the hanging wall, and. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From medium.com
FAULTS IN GEOLOGY. What Are Faults? by ROHIT GURJAR Medium What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall. Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments; normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Deforming of the Earth’s crust PowerPoint Presentation, free What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall the hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. This type of fault can result in significant geological features and can also generate powerful seismic events. These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. in normal faults, the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall (figure 13. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From openpress.usask.ca
13.3 Fractures, Joints, and Faults Physical Geology, First University What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall in normal faults, the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall (figure 13 and figure 14). The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. This motion can be determined by tracing the. If the fault develops in a situation of. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. . What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Use Figure 14.11 (below) and select the proper fault name What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall If the hanging wall moves sideways, parallel. If the fault develops in a situation of. reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall. The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. a reverse/thrust fault is a. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From pungkimilleniumhalle.blogspot.com
Difference Between Hanging Wall And Footwall What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall This motion can be determined by tracing the. They are common at convergent boundaries. If the fault develops in a situation of. a reverse/thrust fault is a geological fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall due to compressional forces, often associated with convergent plate boundaries. the body of rock above the fault is. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT EARTHQUAKES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1946703 What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments; Faults. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.pinterest.com
Earthquake Fault Footwall HangingWall Earthquake fault, Earthquake What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. the. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Structural Geology Stress and Strain PowerPoint Presentation What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall The steep face of an exposed block is called the fault scarp. They are common at convergent boundaries. If the fault develops in a situation of. This motion can be determined by tracing the. the hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. the body of rock above the fault is called the hanging wall, and the body. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Earthquakes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID506706 What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall They are common at convergent boundaries. reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up. The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. Thrust faults are reverse faults that dip less than 45°. This motion can be determined by tracing the. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. . What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From geol319r4.athabascau.ca
Unit 4 GEOL 319 What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. the hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. a reverse/thrust fault is a geological fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall due to compressional forces, often associated with convergent plate boundaries. The. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Folds, Faults, and Geologic Maps PowerPoint Presentation, free What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall the hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. This type of fault can result in significant geological features and can also generate powerful seismic events. This motion can be determined by tracing the. normal faults form when the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. The steep. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Geology 12 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID671456 What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall This type of fault can result in significant geological features and can also generate powerful seismic events. the hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. They are common at convergent boundaries. Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments; normal faults form when the hanging. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From cesqxeqg.blob.core.windows.net
Hanging Wall Definition Geology at Kelly Smart blog What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments; a reverse/thrust fault is a geological fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall due to compressional forces, often associated with convergent plate boundaries. the body of rock above the fault is called the. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From ds.iris.edu
Images courtesy of the Alaska Earthquake Center What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall These are often found in intensely deformed mountain belts. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall. The hanging wall is above the fault plane while the foot wall is below. a reverse/thrust fault is a geological fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall due to compressional. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.
From dxoiowtgp.blob.core.windows.net
What Is A Hanging Wall And A Footwall at Harvey Maxey blog What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall The steep face of an exposed block is called the fault scarp. the hanging wall moves up and over the footwall. Faults are the places in the crust where brittle. Thrust faults are reverse faults that dip less than 45°. the hanging wall moves horizontally, vertically, or in both directions relative to the footwall. The forces creating reverse. What Do You Call A Fault In Which The Hanging Wall Moves Up With Respect To The Footwall.